7-1) Consuming RESTful Web Services
1) Check and see if there is an existing Anypoint
Connector to connect to the service provider.
2) If not, use the HTTP
Request connector.
Walkthrough 7-1:
Consume a RESTful web service
- Create a new flow to call a RESTful web service
- Use an HTTP Request endpoint to consume a RESTful web
service
- Use DataWeave to transform the JSON response into JSON
specified by an API
Image: Global
Element: United HTTP Request Configuration
Image: United REST
Request
Image: x+y? - examining the REST API Message Payload
Note: DataWeave Transform Message allows you
to load examples (like JSON examples) and graphically map elements.
7-2) Passing
arguments to RESTful Web Services
Passing data to a RESTful web service:
- For an HTTP Request endpoint, you can add parameters
- Send form parameters with a request by setting them in
a payload
- Include attachments by adding an Attachment transformer
to your flow
Image: Passing data
to a RESTful web service
Walkthrough 7-2:
Pass arguments to a RESTful web service
- Modify the HTTP Request endpoint to use a URI parameter
- Set the destination to a static value
- Create a flow variable to store the value of a query
parameter
- Set the URI parameter to the dynamic value of this flow
variable
Image:
getUnitedFlightsFlow
Image: Capturing Airport
Code in a Variable
Modifying (Airport) code so we don’t get an error if code
is not specified in the request:
Value: #[message.inboundProperties.'http.query.params'.code
== empty ? 'SFO' : message.inboundProperties.'http.query.params'.code]
Image: United REST
Request
7-3) Consuming
RESTful web services that have RAML definitions
A RAML location (local file or external URI) can be
specified for a HTTP Request connector.
After you specify a RAML location, all fields will be
automatically populated based on what’s specified in the RAML.
Walkthrough 7-3:
Consume a RESTful web service that has a RAML definition
- Create a new flow to call a RESTful web service that
has a RAML definition.
- Select the web service resource from the list provided
by Anypoint Studio from the RAML file.
- Use DataWeave to transform the JSON response into JSON
specified by an API.
Image: Transform
Message: Populating null with a value
7-4) Consuming
SOAP web services
Mule’s SOAP support is based on Apache CXF
- CXF is a web services framework in Java for SOAP
messaging
- Handles all serialization and deserialization
- Handles all SOAP envelope and namespace processing
- Developer only sees POJOs (Java Object) etc. - not SOAP
XML
Consuming SOAP web services:
If there is not an
existing Anypoint Connector to the Service Provider ...
- Use the Web
Service Consumer connector (provide
the WSDL)
- If you need more features, use the CXF component (also used to
expose an endpoint as a SOAP service)
Walkthrough 7-4:
Consume a SOAP Web Service
- Create a new flow to call a SOAP web service
- Use a Web Service Consumer endpoint to consume a SOAP
web service
- Use DataWeave to transform the XML response into JSON
Image: Configuring
a (Global) Web Service Consumer
Image: Web Service
Consumer configuration (for SOAP)
Image: Mapping XML
to JSON in DataWeave Transform Message
7-5) Passing
arguments to SOAP web services with DataWeave
Walkthrough 7-5:
Pass arguments to SOAP web service
- Change the web service operation invoked to one that
requires a destination as an input argument.
- Set a flow variable to the desired destination.
- Use DataWeave to pass the flow variable to the web
service operation.
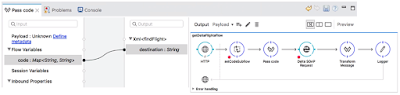
Image:
setCodeSubflow -> Pass code -> Delta SOAP Request
Image: DataWeave
knows the input and knows the output needs to be XML












Comments
Post a Comment