Objectives:
- Route messages based on conditions
- Multicast messages
- Filter messages
- Validate messages
Anypoint Studio: Mule Palette: Flow Control:
- APIkit Router
- Choice
- Collection Aggregator
- Collection Splitter
- Custom Aggregator
- First Successful
- Message Chunk Aggregator
- Message Chunk Splitter
- Resequencer
- Round Robin
- SOAP Router
- Scatter-Gather
- Splitter
9-1) Routing messages
based on conditions
The Choice router:
- Sends the message to one route based on conditions
Walkthrough 9-1:
Route messages based on conditions
- Use a Choice router
- Set the router paths
Image: Route
messages based on conditions
Image: Placing
within a Choice router: Look for the thick black vertical line
Image: Configuring
the Choice router
9-2) Multicasting
messages
The Scatter-Gather router:
- Sends the message to each route concurrently and
returns a collection of all results
Walkthrough 9-2:
Multicast a message
- Use a Scatter-Gather router to concurrently call all
three flight services
- Use DataWeave to flatten multiple collections into one
collection
- Use DataWeave to sort the flights by price and return
them as JSON
Image: Multicast a
message
Image: And modify
the Default to use the getAllAirlineFlightsFlow
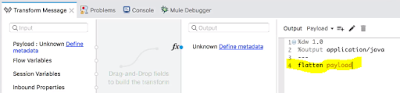
To flatten the payload, in ‘Transform Message’ enter “flatten payload”.
Image: Flatten
Payload (in the Transform after the Scatter-Gather)
Within ‘Transform Message’ output use Ctrl+Space to bring up some
autocomplete.
Image: Configuring
‘Transform Message’ after the Choice.
Image: Flight_pogo
JAVA object being configured in the ‘Transform: Define metadata’ (needs com.mulesoft.training.flight)
Note: After making
changes to Define metadata, clear out the old metadata (in the right side
Output) and redo the mappings.
9-3) Filtering
messages
- Determine whether a message can proceed in a Mule flow.
- By default filtered messages are dropped and processing
of the message ends:
--- Keeps subsequent processors from receiving irrelevant
or incomprehensible messages.
--- Filters can be configured to throw an exception.
Anypoint Studio: Mule Palette: Filters (Expression and Payload are most often used):
- And
- Custom
- Exception
- Expression
- Filter Reference
- Idempotent Message
- Message
- Message Property
- Not
- Or
- Payload
- Regex
- Schema Validation
- Wildcard
Walkthrough 9-3:
Filter messages
- Use the Payload filter
- Create and use a global filter
Image: Filter
messages (Global Element Payload Filter)
9-4) Validating
messages
The main advantage over using filters is traceability:
- Filters all raise identical exceptions, making it hard
for you to know where the exception was caused.
- Validators raise an exception with a meaningful message
attached.
Use the ‘Validation’
component in the Mule Palette.
Select type of validation (‘All’ to create a list of
validations to execute).
Examples: All,
Custom Validator, Is Email, Is Empty, Is False, Is IP...
2 ways to use validators:
- Validator component (within ‘greater than bracket’ ...
/ ‘less than bracket’):
validation:is-email
email=”mule@mulesoft.com”
- Through MEL:
#[validator.validateEmail('mule@mulesoft.com')]
Walkthrough 9-4:
Validate messages
- Use the Validation component to throw an exception
- Catch the ValidationException in the global exception
strategy
Image: Catching the
ValidationException in the global exception strategy









Comments
Post a Comment